Cervical osteochondrosis (cervical osteochondrosis) is a chronic degenerative disease of the spine, in which the structure of the vertebrae is distorted, the integrity of the intervertebral structures is disrupted, and the roots of the spinal cord are damaged.
Important to know!Osteochondrosis is not a death sentence.There is always an opportunity to alleviate the aggravation of the process and control the progression of changes in the spine.In the most advanced cases, neurosurgical interventions are possible.However, this does not exclude the possibility that the disease can be “triggered”.It is very important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of osteochondrosis to diagnose the disease and prescribe preventive measures at an early stage!
Reasons for development
The anatomical structure of the spine suggests that the cervical spine has the greatest mobility, and in the cervical spine the vertebrae are the smallest.These two factors make the neck one of the “weak areas” of the spine.
The main reasons for the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are a combination of the following unfavorable factors:
- Incorrect posture and neck posture (including when working at the computer).
- High physical stress on the cervical spine and shoulder girdle.
- Spinal injuries...
- Age-related changes in the tissue of the intervertebral structures.
- Wrong diet, too few essential vitamins and minerals.
It should be said that almost every person develops osteochondrosis with age;According to some researchers, it is “a form of retaliation for walking upright.”However, in the modern world with its fast life, sedentary lifestyle and long work at the computer, cervical osteochondrosis ranks first among spinal problems.
Symptoms
Symptoms can vary greatly depending on the extent of spinal damage, the severity of degenerative changes, the individual characteristics of the human body and many other factors.Neurologists prefer to distinguish three main symptom complexes that occur with cervical osteochondrosis, as well as their combination:
- Vertebrogenic cervicalgia.
- Vertebrogenic cervicocranialgia.
- Vertebrogenic cervicobrachialgia.
By the names we can identify the main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis.With cervicalgia, the main complaint is the pain directly in the neck;in vertebrogenic cervicocranialgia, the pain in the neck also extends to the head;In cervicobrachialgia, pain in the neck spreads to one or both arms, cramps also occur in the arm, numbness and a crawling feeling in the arms may occur.In all cases of osteochondrosis, the following symptoms may occur: tension in the neck muscles, crunching in the neck, restricted movement in the neck.
Radiculopathy
In severe osteochondrosis, complicated by bulges or herniated discs, a so-called radiculopathy can form: a dysfunction of a specific spinal root with the development of weakness of the innervated muscles, their weight loss and sensory impairment.
Diagnostics and X-ray signs
Osteochondrosis is an X-ray diagnosis, since a detailed clinical picture is present only at the moment of exacerbation, while when a person is in complete subjective well-being, changes in the spine may occur.Without an X-ray examination, one can only speak of a suspicion of osteochondrosis, since similar symptoms can also be caused by other diseases (myositis, vertebral neoplasia, etc.).
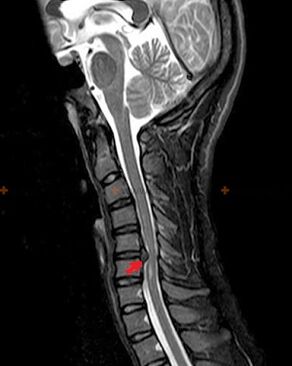
To diagnose osteochondrosis, the following examination methods are used: radiography (preferably with functional tests), MSCT and MRI.The latter study is the most preferable as it allows a very clear visualization of the condition of the intervertebral structures.
The X-ray signs of osteochondrosis include the following changes in the spine:
- Reduced height of the intervertebral discs.
- Presence of marginal bone growths.
- Violation of the position of the vertebrae relative to each other.
- Deformations of vertebral bodies and arches, etc.
The presence of the changes described above, as well as changes in the structure of the intervertebral disc detected by MSCT and MRI, serve as reliable signs of the presence of osteochondrosis.
Treatment
Treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at all aspects of the pathogenesis of clinical manifestations.Chronic dystrophic changes during exacerbations lead to inflammation of the spinal cord roots, which in turn causes reflex pain.Pain is a signal for the muscles to develop a protective response - muscle spasms.Muscle spasms bring the vertebrae closer together and increase compression (compression) and inflammation of the roots.The circle is closed.That is why it is necessary to eliminate inflammation, pain and muscle spasms and protect the roots from inflammatory effects.
There are drug and non-drug treatment methods.They change partially when certain symptoms predominate, but have a general pattern.
Medication
Anti-inflammatory drugs (aceclofenac, ketoprofen, meloxicam, diclofenac, etc.), muscle relaxants (tolperisone hydrochloride, baclofen, tizanidine) and neuroprotective drugs (complex preparations of B vitamins and thioctic acid) are used.
Non-medicinal
Includes massage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy.Massage for cervical osteochondrosis is very effective in relieving muscle spasms, improving blood circulation in the spinal tissues, thereby reducing the severity of the inflammatory process.Physiotherapy can be aimed at both relieving pain (electrophoresis with analgesics) and relieving muscle tension (diadynamic currents).Therapeutic exercises are a unique and extremely effective method of disease prevention.A set of exercise therapy exercises for cervical osteochondrosis can be found here.
Folk remedies
Among the traditional methods of treatment, it is worth highlighting the use of various warming compresses based on water and alcohol, which can reduce the intensity of neck pain and relieve inflammation.The “dry heat” method has also proven successful, the essence of which is to heat salt or sand in a cloth bag and then apply it to the area of pain.
Traditional methods of treating osteochondrosis of the cervical spine include the use of applicators - special devices or simply needle-coated tissue surfaces.Applying moderate pressure to the neck area, as well as simply lying on such a surface for 10-15 minutes, leads to reflexive relaxation of the neck muscles and annoying pain relief.
























